(AI-generated image)
Intro
In today’s interconnected world, integrating with a vast ecosystem of SaaS providers presents a significant challenge. It is not just about understanding and creating OpenAPI REST clients for numerous APIs, but also mapping them to our internal domain model. The real hurdle lies in the continuous maintenance of both the client and the mapping code as these third-party SaaS APIs evolve.
Scenario
Imagine we’re building a neobank in the UK. A key feature of our app is providing users with a unified view of their accounts and balances across their various bank accounts. Fortunately, all major UK banks adhere to the OpenBanking API specification. To streamline the integration process, we can leverage an MCP server for OpenAPI. This server can provide a GenAI LLM, such as GPT or Claude, with enhanced context about the API. This additional context empowers the LLM to generate higher-quality code for the HTTP client and the mapping to our internal domain model.
What is MCP?
Model Context Protocol or MCP offers a standardised method for AI agents to interact with external systems, abstracting away their underlying implementation details. Think of it as the “USB-C” for AI interactions.
Solution
Ensure that MCP server for OpenAPI is installed. Now, when crafting your prompt within Copilot or Cursor, you can add more context to your prompt by using the newly available ‘#getApiOverview’ LLM tool from the OpenAPI MCP server.
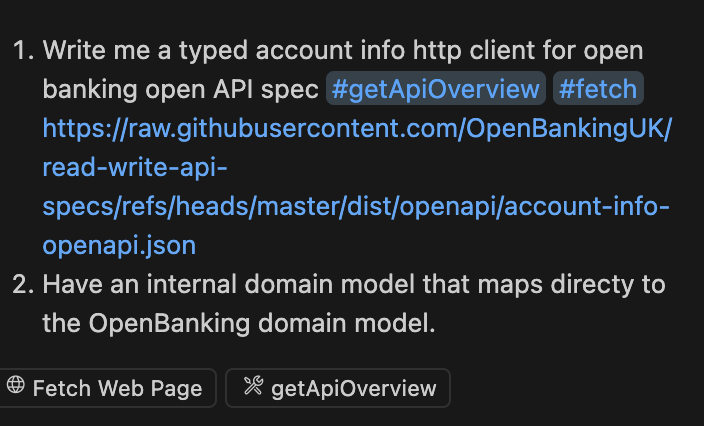
By using this tool, Copilot (or your chosen LLM) can leverage the OpenAPI MCP server to gain a deeper understanding of the OpenAPI specification of OpenBanking in this case. This enhanced context enables it to generate a more robust and accurate typed HTTP client and the corresponding mapping code to your internal domain model.
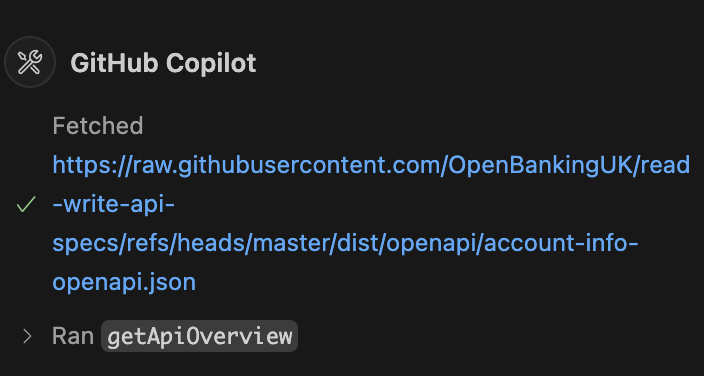
The result? Autogenerated, type-safe HTTP client code and mapping logic—significantly simplifying and accelerating the integration process.
The Integration Challenge
Beyond the initial work of creating OpenAPI REST clients and mapping them to internal models, the real ongoing burden is maintenance as these third-party APIs evolve. The financial technology world moves at lightning speed, with APIs constantly evolving to offer new features, improve security, and fix bugs.
For the UK neobank example, we need to stay on top of changes across all OpenBanking API implementations because staying current with these changes isn’t just good practice, rather it is essential to maintaining service reliability and compliance. When a major bank updates its authentication requirements or adds new transaction categories, we need to know immediately and adapt our integration accordingly.
Enter Doc-Monitor: An MCP-Powered Solution
This is where Doc-Monitor shines. Built on the MCP, our tool continuously monitors API documentation for changes, automatically crawls and indexes content, and provides powerful RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) capabilities that empower AI assistants to understand these evolving APIs.
What Makes Doc-Monitor Different?
Feature | Doc-Monitor | Cursor Documentation/Context7 |
Documentation Ingestion | Automatic detection of documentation types (OpenAPI, sitemaps, webpages) with appropriate crawling strategy | Manual addition of URLs through settings; requires user to input URLs |
Change Detection | Proactive monitoring with automatic detection of documentation changes on command | Re-indexing on command; no specific change detection |
Change Impact Analysis | Analyses significance of changes; identifies breaking changes and their potential impact on integrations | No change impact analysis |
API Monitoring | Complete API documentation monitoring upon manual trigger with impact assessment | Not an API monitoring tool; primarily for reference |
Target Use Case | Enterprise API integration teams needing to track changes across multiple external APIs | Individual developers referencing documentation within IDE |
Business Intelligence | Provides strategic insights on API changes and their business impact | Developer-focused with minimal business intelligence |
Real-World Impact: OpenBanking API Monitoring
Let’s revisit the UK neobank scenario. With Doc-Monitor in place:
1. We monitor all major UK banks’ OpenBanking API documentation
2. When one of such bank updates their transaction categorisation schema, Doc-Monitor identifies the change immediately with just one prompt from the developer’s end
3. The system analyses the impact and determines that it affects our transaction reconciliation system
4. Our developers receive not just an alert, but contextual information about what exactly changed and how it affects the codebase
The MCP Advantage
The true power of Doc-Monitor comes from its implementation of the MCP. For our neobank developers, this means:
1. Enhanced Context in AI Coding Tools: When a developer asks “How do I format the new transaction categories from a financial institution?” in their AI coding assistant, the assistant can query Doc-Monitor via MCP to provide up-to-date, accurate answers.
2. Automatic Code Generation: The assistant can generate updated client code and data mappings for the new API version, with full context about what changed and why.
3. Documentation Integration: Explanations about API changes can be automatically incorporated into internal documentation, keeping the entire development team informed.
Beyond Banking: API Ecosystem Monitoring
While the neobank example is compelling, Doc-Monitor’s capabilities extend to any organisation interfacing with multiple APIs:
E-commerce platforms integrating with payment processors and shipping providers
Healthcare systems connecting to insurance and medical record APIs
Enterprise software leveraging cloud service provider APIs
The Future of Integration
As APIs continue to proliferate and evolve, the organisations that can adapt quickly to changes will have a significant competitive advantage. MCP-powered Doc-Monitor represents a new approach to this challenge, the one where API documentation changes are not just detected but understood and acted upon with the help of AI.
For our neobank and countless other businesses, this means faster updates, fewer integration issues, and ultimately a better experience for end users who never have to know about the complex API ecosystem working behind the scenes.
Acknowledgments: We would like to thank Ravindra Jaju and Akshay Karle for their effort in reviewing this article.




